Dim
Improvement of children and youth’s health
- Home
- Health plus
- Improvement of children and youth’s health
Improvement of children and youth’s health
01Developmental characteristics in childhood/adolescence
- Generally, childhood refers to ages 6 to 12. It is the period when a child starts attending elementary school and comes to spend much time with people other than his or her family outside the boundaries of home. During this period, a child comes to recognize his/her role, care for others, and learn about social cooperation as well as a sense of community through group acts or plays. The child’s school life and relationship with peers come to have a decisive impact on the child’s growth and personality development.
- Adolescence refers to ages from 12-13 to 19-20 when secondary sex characteristics appear. Early in this period, adolescents go through rapid physical growth and come to have reproductive ability. They display an inclination toward egocentrism and idealism, feel resistant to adults’ values and beliefs, and engage in a variety of experiments concerning their future roles. Thus, they can be easily exposed to situations that may do harm to their health. As such, it is important to provide them with preventive guidance.
Growth and developmental characteristics in childhood/adolescence
| Major features | Explanation | Points to be considered for health promotion |
|---|---|---|
| Development of muscles and skeleton; rapid physical growth |
|
|
| Permanent teeth |
|
|
| Displaying secondary sex characteristics; sexual maturity |
|
|
| Development of a sense of community with peers |
|
|
02Health promotion in childhood/adolescence
(1)Maintaining the right physical posture
- School-age children are still in the stage of skeletal development. If they keep a wrong posture for a long time, such may lead to a deformation of the skeleton. It is important to have them develop the habit of maintaining a proper posture to help them grow healthy.
- As they spend much time sitting at a desk, it is important to have them use a desk/chair fit for their height and help them build the habit of sitting with proper posture.
- < Taking a proper posture when sitting at a desk for health >
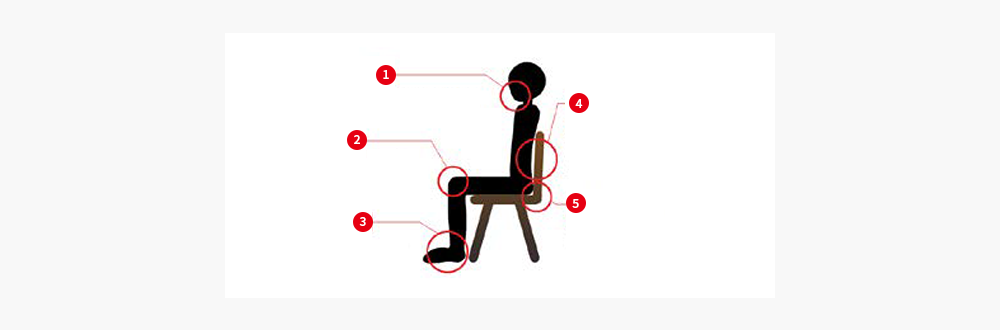
- 1Chin : Pull your chin slightly downward.
- 2Knees : The legs should create a right angle at the knee, with the thighs parallel to the floor.
- 3Soles : Have your soles touch the floor.
- 4Waist : Keep waist to back of seat, and make sure your body is not bent.
- 5Hips : Sit on the edge of the chair.
Scoliosis
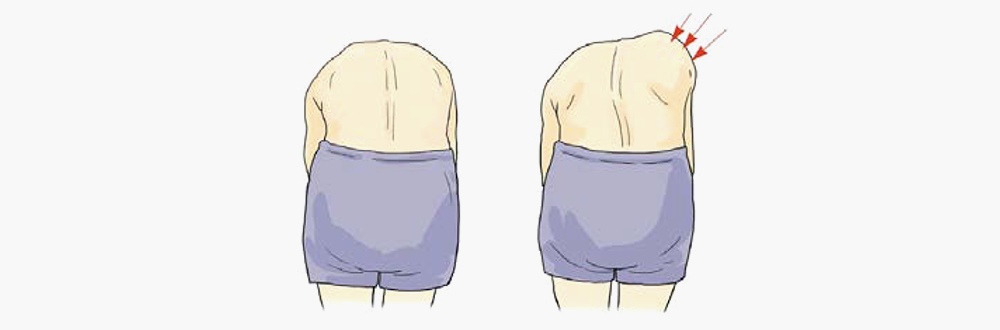
- < Comparison between a person with a normal spine (left) and one with scoliosis (right) >
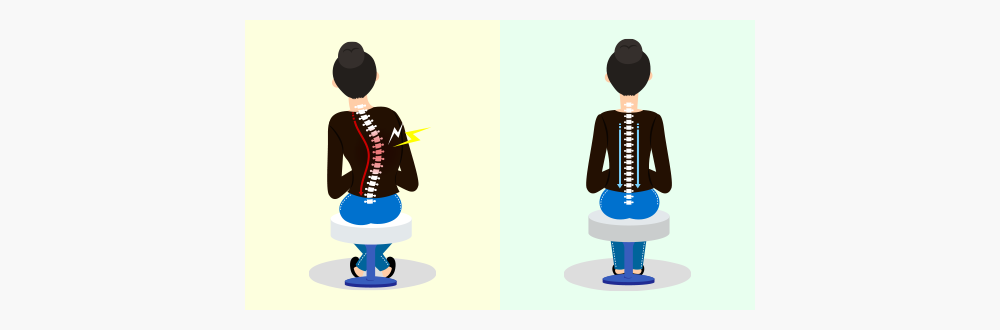
- Scoliosis refers to a condition characterized by the sideways curvature of the spine or backbone like the letter “C” or “S.”
- Recently, there has been an increase in the number of young people suffering from this condition due to their frequent use of smart phone or wrong posture when sitting.
- If detected early, scoliosis can be corrected/cured within a short period of time. It is recommended that you check from time to time whether your children have this condition so that they can see a doctor and set their condition right early.
Scoliosis signs and symptoms
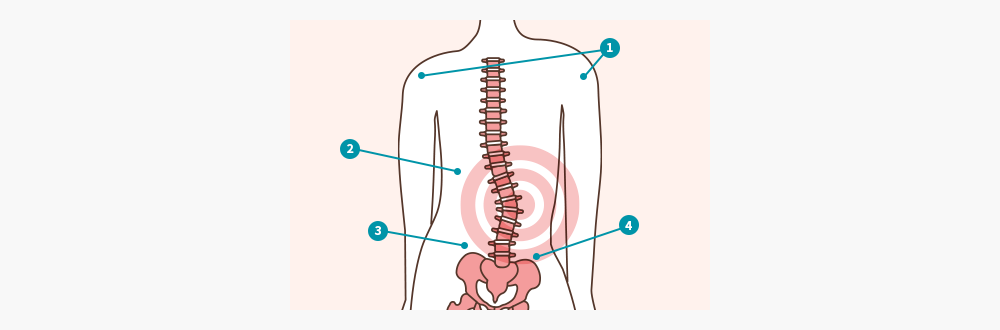
- ① Uneven shoulders, ② Shoulder blade protruding, ③ Curve in spine, ④ Uneven hips
- Uneven shoulders, curve in spine, and uneven hips
- Rotated ribcage; ribs and shoulder blade protruding
- The waistband of the pants or skirt appears uneven; Shoe soles wear out faster on the outside of the foot
- The distance between the arm and torso is larger on one side than the other.
(2)Teeth management
It is important to manage your teeth in childhood/adolescence when primary teeth are replaced with permanent teeth, as the quality of your life in later years depends on the status of your teeth.
How to brush your teeth and use floss properly
- Tooth brushing is the first thing you need to do to prevent tooth decay. We recommend brushing your teeth at least three times a day, within three minutes of eating a meal, and spending at least three minutes brushing your teeth. It is particularly important to brush your teeth before going to bed. Replace your toothbrush with a new one every two/three months.
- You need to brush all parts of each tooth meticulously. You should also brush your tongue when brushing your teeth.
- Use dental floss after brushing the teeth. Children cannot be expected to use dental floss properly alone until they are eight or nine years old. Parents should help them use it each time they brush their teeth.
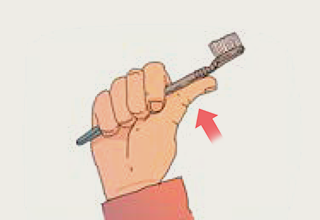
Right tooth brushing
- 1.Hold your toothbrush like this.
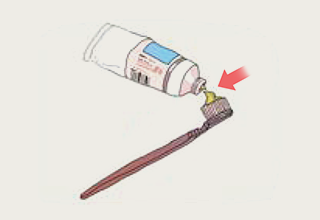
- 2.Apply slight pressure so that toothpaste is dispensed onto the toothbrush.
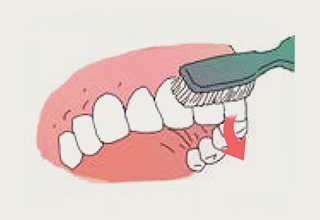
- 3.For the outside surfaces of the front teeth: Place your toothbrush on the part between the teeth and the gums and then move it downward in a gentle circular motion.
- 4.For the front lower teeth: Place your toothbrush on the part between the teeth and the gums and then move it upward.
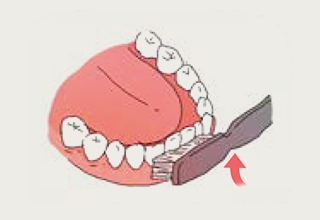
- 5.For the inside surfaces of the front teeth: Place your toothbrush vertically and move it from inside out.

- 6.For the outside surfaces of the molars: Place your toothbrush on the part between the teeth and the gums and move it toward the top part in a gentle circular motion.
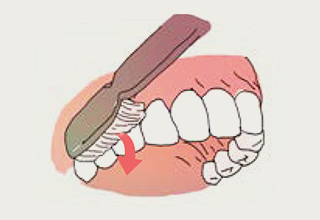
- 7.For the top part of the molars: Brush the back and front ten times.
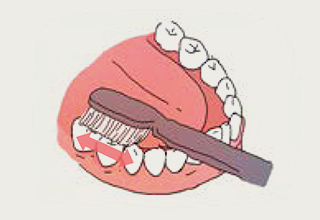
- 8.For the inside surface of the molar: Place your toothbrush on the part between the teeth and the gums and move it toward the top part in a gentle circular motion.
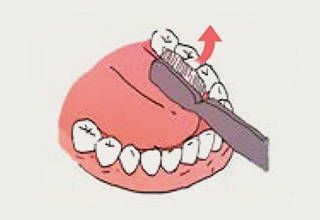
- 9.For the tongue: Place your toothbrush on the deep side of the tongue and move it as indicated in the picture.

Preventing tooth decay
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, should be treated in a timely manner and taken care of continuously to prevent dental erosion.
- Brush your teeth the right way.

- Be sure to see a dentist when you have a problem with a tooth.

- Avoid sweet food and carbonated drinks. Eat enough vegetables, dairy products, and fruits.

- The use of fluoride toothpaste helps you prevent tooth decay.

- Periodic visits to a dentist allow detecting tooth decay early and enhance the effect of dental treatment.

(3)Sexual health management
- With the appearance of secondary sex characteristics in young people, they come to have more interest in sex. In early adolescence, they come to have sexual fantasies and explore the opportunity to go on a date or have a sexual relationship, developing sexual affinity with those of the opposite sex based on their values, beliefs, or traditions.
- They often engage in reckless sexual acts out of their belief in their invincibility, which is part of the psychological development characteristics of the period, or out of pressure from peers or in an attempt to display their “maturity.”
- Young people engaging in sexual acts are likely to be exposed to a variety of risk factors threatening sexual health such as pregnancy, sexually transmitted diseases, etc. due to the vulnerability of their sexual genitals.
- We need to help young people put off their sexual acts until they are fully ready physically, cognitively, and emotionally for a mature sexual relationship and they can foresee the results of acts such as those.
Male and female genitalia
- Structurally, the female genitalia is much more vulnerable to external infection than the male one. Women cannot see most parts of their own genitalia directly as they are inside of their body. When there is a problem in the female genitalia, the symptom does not show immediately. In many cases, a disease is already at an advanced stage when a symptom manifests. Accordingly, women need to maintain their sexual health through more positive self-management and periodic health checkups.
Difference between male and female genitalia
-
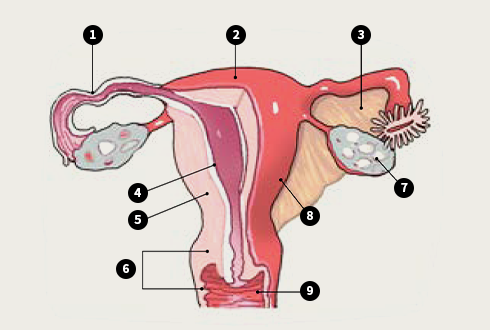
- ① fallopian tubes, ② base of the uterus, ③ ligament, ④ endometrium, ⑤ muscles of the uterus, ⑥ cervix , ⑦ ovary , ⑧ uterus , ⑨ vagina
Female genitalia- Women cannot see their uterus directly, as it is inside of their body.
- The fallopian tubes are open in the abdominal cavity. Their urethra is shorter than that of males and separated from the vagina, which is the muscular tube leading from the external genital to the cervix, and vulnerable to intrusion by outside microbes.
-
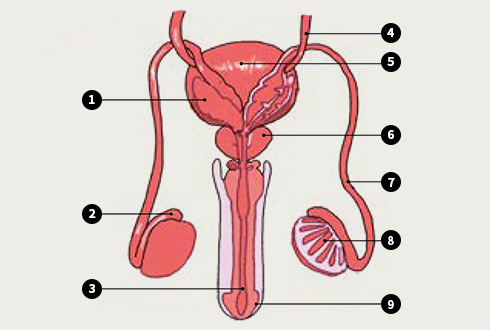
- ① seminal vesicle, ② epididymis , ③ urethra, ④ ureter, ⑤ bladder , ⑥ prostate , ⑦ vas deferens , ⑧ testicles , ⑨ glans
Male genitalia- Male genitalia are composed of a closed tube leading from the testicles to the urethra.
- Males’ urethra is longer than that of females. Males’ urethra also serves as the passage for semen, and it is less vulnerable to intrusion by outside microbes compared to that of women.
Health management of female genitalia
- Wear breathable cotton underwear.
- Do not wear tight underwear.
- Do not hold your urine.
- Wipe front to back in the toilet so as not to have your vagina contaminated.
- When washing your genitalia, use neutral soap to maintain acidity. Wash three/four times a week using the shower head front to back.
- When replacing a sanitary pad or a tampon, be sure to wash your hands first.
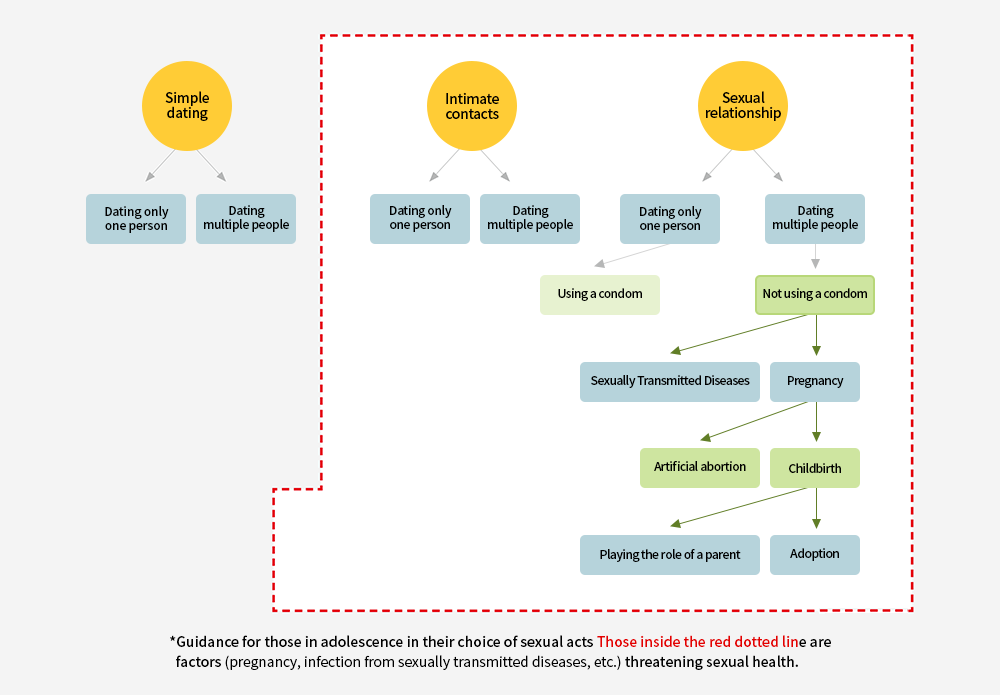
Guidance on the choice of sexual acts
- During adolescence, you are likely to experience difficulties predicting your future and adjusting yourself to your current circumstances. Hopefully this guidance will help you make the right choice when it comes to sexual acts.
Guidance for those in adolescence in their choice of sexual acts
Self-management for the enhancement of sexual health
- 1Self-exam of your pudenda
- Women who have had a sexual relationship or who are sexually active should engage in this self-exam monthly.
- Pudendal disorder can be easily confirmed through visual inspection or manual palpation. Periodic pudenda self-exam helps you find a problem in your genitalia early and goes a long way in preventing the spread of sexually transmitted diseases.
Pudenda self-exam methods- Items you need to prepare: mirror with handle
- How to do it: Find a bright and quiet place, assume a position that will allow you to look at your pudenda through a mirror, and take the following steps:
- 2Testicular self-exam
- Use this method to discover early and prevent testis cancer. Engage in this method once a month, spending about 3 minutes for careful manual palpation.
- Testicular cancer can occur in any age group, but recently there has been a report on an increase in the number of those aged 15~35 getting it. If you find it in its early stage, the odds of being cured are good.
How to do a testicular self-exam- Item you need to prepare: a mirror
- Proceed as follows:
- 3Breast self-exam
- Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that forms in the breasts. It ranks No. 1 among cancers affecting Korean women. Recently, there has been a sharp increase in the number of cases of breast cancer in Korean women supposedly due to changes in life patterns and dietary habits.
- Breast self-exam is deemed more important considering the fact that women get breast cancer at an increasingly earlier age.
- Where cancerous growth is confined to the breasts, breast cancers are easy to remove and treat, and patients’ survival rate is high. If cancerous growth has been metastasized to neighboring tissues, however, it may threaten the patient’s life.
- Breast cancer can be found early through self-exam.
- Breast self-exam: Do a breast self-exam 5 to 7 days after finishing your menstrual period, when the breasts feel softest. If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or menopausal, set a day each month and do it.
- A.How to improve your breast health
- Do a self-exam of the breasts each month to check their health status.
- If you feel a lump in the breasts or there is a change in the shape or skin color of your breasts, see a doctor.
- Prevent breast cancer by avoiding what are known as risk factors.
- B.Breast cancer risk factors
- Changeable breast cancer risk factors
- Recent history of taking oral contraceptive pills
- Drinking alcohol
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Highly intense radiation to the chest
- Unchangeable breast cancer risk factors
- History of breast cancer, etc.
- Menstrual history
- Genetics
- Pregnancy/Breastfeeding history
- High levels of estrogen/testosterone
-
- C.Breast self-exam/manual palpation
- Items you need to prepare: full-length standing mirror, bed, pillow, gown
- Proceed in the following order: visual inspection → manual palpation → squeezing the nipples.
- Do visual inspection and then manual palpation, putting your fingers on your breast and pressing as if drawing a circle to check whether there is an unusual lump.
- When doing manual palpation of the breasts, you better lie down as it will cause the breast tissues to spread evenly throughout the breasts.
- Check whether you feel an unusual lump in the breasts. You may choose to do manual palpation, using moistened/soaped fingers, while standing in a shower.
- Finally, squeeze your nipples to check whether there is liquid flowing out.
How to do breast self-exam/manual palpationDoing a breast self-exam in a standing position- 1Lift your arm and palpate, starting from the part right below the armpit to the lower end of the breast.
- 2Prop up the lower end of a breast with one hand and palpate using the other hand.
- 3Do the same for the other breast.
Doing a breast self-exam in a lying position- 1Lie down with the arm lifted up. Put a pillow or a pad under the shoulder. Then, start palpating from the part right below the armpit to the lower end of the breast.
- 2Do the same for the other breast.
Checking whether fluid comes out of your nipples by squeezing them- 1Use the thumb and forefinger to squeeze the nipple and check whether fluid comes out.
- 2Do the same for the other breast.
- 4HPV vaccination to prevent cervical cancer
- Cervical cancer refers to the malignant tumor forming on the cervix, which is the entrance to the uterus.
- Cervical cancer is found in more than 3,000 women per year in Korea, and 900-plus women die of it each year.
- The main cause of cervical cancer is Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection spreading through sexual contact. High-risk types of HPV are found in 99 percent of cervical cancer patients. Cervical cancer can be prevented effectively through HPV vaccination.
- Adults can maintain their immunity with three vaccinations, but children under the age of 12 display a high level of immunity with only two vaccinations. Especially, two vaccinations before one’s first sexual contact bring about the best possible effect in the prevention of cervical cancer.
- In Korea as well as in most other countries, the State provides free preventive vaccination for young girls under the age of 12.
- You can see the details of the content of the State-provided HPV vaccination in the website of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency (KDCA) (https://www.kdca.go.kr/gallery.es?mid=a20503010000&bid=0002&list_no=145640&act=view).

This work can be used according to the “KOGL (Korea Open Government License) Type 4: Source Indication+Prohibition of Commercial Use+Prohibition of Change” condition.
Dim
Dim
딤영역
딤영역